From Command-Line to Bash Script
Bash란 ? Bourne Again Shell 의 약어로, 유닉스 및 맥 컴퓨터 시스템의 기본값 입니다.
유닉스 시스템은 인터넷과 서버의 중추로 대규모 ML 모델 실행과 데이터 파이프 라인 및 아키텍처에 중요합니다.
모든 클라우드에는, 명령 줄 인터페이스가 있습니다.
Bash를 사용하는 이유!
- Bash 명령을 하나씩 복사하여 붙여 넣는 대신 단일 명령으로 프로그램을 저장하고 실행 가능
- 강력한 프로그래밍 구성에 쉽게 액세스 할 수 있다.
Shell commands refresher
grep: 정규식 패턴 일치를 사용하여 다른 프로그램이나 명령에서 입력한 내용을 필터링cat: 줄 단위로 사용할 파일 내용을 출력tailorhead: -n를 사용하여 첫 번째, 혹은 마지막 줄을 제공wc: -w -l 을 사용하여 단어 또는 줄 수를 계산sed: 정규식 패턴 일치를 사용하여 문자열 대체를 수행
Bash script anatomy
bash ooo.sh 를통해서 실행
#!/usr/bash
echo "Hello world"
echo "Goodbye world"#!/usr/bash
cat animals.txt | cut -d " " -f 2 | sort | uniq -c# sed 명령어
sed 's/1/2/g' <파일> # 1을 2로 바꿔서 출력
sed 's/1/2/gi' <파일> # 1을 2로 바꿔서 출력(대소문자 무시)Standard streams & arguments
- STDIN (standard input) - A stream of data into the program
- STDOUT (standard output) - A stream of data out of the program
- STDERR (standard error) - Errors in your program
."
echo $rightnow_doublequote
echo $rightnow_parenthenses
[output]
The date is Mon 2 Dec 2019 14:13:35 AEDT.
The date is Mon 2 Dec 2019 14:13:35 AEDT.Numeric variables in Bash
숫자 변수로 작업하는 것은 Bash에 내장되어 있지 않음
expr 1 + 4
[output]
5단, 소수계산은 되지 않음
이럴땐 bc (basic calculator)를 사용하면 됨

echo "scale=3; 10 / 3" | bc
[output]
3.333model1=87.65
model2=89.20
echo "The total score is $(echo "$model1 + $model2" | bc)"
echo "The average score is $(echo "($model1 + $model2) / 2" | bc)"Creating an array in Bash
bash에서 배열을 생성하는 법은 다음과 같다.
- 값 없이 배열만 선언
declare -a my_first_array - 선언과 동시에 값을 삽임
my_first_array=(1 2 3)# 등호주위에 공백을 넣지 말기!
다른 프로그래밍 언어들과 다르게 bash는 쉼표가 아닌 공백으로 배열 요소를 구분합니다.
my_array=(1 3 5 2)
echo ${my_array[@]}
[output]
1 3 5 2@를통해 배열 모든 요소를 출력할 수 있습니다.
echo ${#my_array[@]}
[output]
4# 을통해 배열의 길이를 알 수 있습니다.
my_array=(15 20 300 42)
echo ${my_array[2]}
[output]
300zero-indexing 사용!
my_array=(15 20 300 42)
my_array[0]=999
echo ${my_array[0]}
[output]
999my_first_array=(15 20 300 42 23 2 4 33 54 67 66)
echo ${my_first_array[@]:3:2}
[output]
42 23다음과 같이 인덱싱으로 출력 가능 [@]:시작번호:출력하고자하는갯수
my_array=(300 42 23 2 4 33 54 67 66)
my_array+=(10)
echo ${my_array[@]}
[output]
300 42 23 2 4 33 54 67 66 10
-----------------------------------------
# 괄호로 묶지 않고 더할 경우 다음과 같이 됨
my_array=(300 42 23 2 4 33 54 67 66)
my_array+=10
echo ${my_array[@]}
[output]
30010 42 23 2 4 33 54 67 66다음과 같이 배열에 추가할 수 있음
declare -A city_details # Declare first
city_details=([city_name]="New York" [population]=14000000) # Add elements
[output]
echo ${city_details[city_name]} # Index using key to return a valuebash 연관배열(딕셔너리형태) 만드는법은 다음과 같습니다.
echo ${!city_details[@]} # Return all the keys다음과 같은 방법으로 키를 출력할 수 있습니다.
If statements
if [ Condition ]; then
# Some Code
else
# Some other Code
fiif 조건 대괄호 안에 양쪽 공백이 필요하며, ; 또한 필요함!
x="Queen"
if [ $x == "King" ]; then
echo "$x is a King!"
else
echo "$x is not a King!"
fi사용 가능한 조건 부호
><=!=-eq: equal to-ne: not equal-lt: less than-le: less than or equal to-gt: greater than-ge: greater than or equal to-e: file exists-s:file exists and has size greater than zero-r: file exists and readable-w: file exists and writable&&||
등등 사용가능
For loops & While statements
for x in 1 2 3
do
echo $x
donedo 와 done이 있다는 것이 파이썬과의 차이점
for x in {1..5..2}
do
echo $x
donerange 설정법은 다음과 같이 .. 으로 나타냄
for ((x=2;x<=4;x+=2))
do
echo $x
done다음과 같이도 나타낼 수 있음
for book in books/*
do
echo $book
donefor book in $(books/ | grep -i 'air')
do
echo $book
done$() 을통해서도 반복문 가능
x=1
while [ $x -le 3 ];
do
echo $x
((x+=1))
doneCase statements
case 'STRINGVAR' in
PATTENRN1)
COMMAND1;;
PATTERN2)
COMMAND2;;
*)
DEFAULT COMMAND;;
esac
-----------------------------
case $(cat $1) in
*sydney*)
mv $1 sydney/ ;;
*melbourne*|*brisbane*)
rm $1 ;;
*canberra*)
mv $1 "IMPORTANT_$1" ;;
*)
echo "No cities found" ;;
esacFunctions
bash의 기본 함수 틀은 다음과 같다.
function_name() {
#function_code
return #something
}
---------------------------
temp_f=30
function convert_temp() {
temp_c=$(echo "scale=2; ($temp_f - 32) * 5 / 9" | bc)
echo $temp_c
}
convert_tempfunction print_filename {
echo "The first file was $1"
for file in $@
do
echo "This file has name $file"
done
}
print_filename "LOTR.txt" "mod.txt" "A.py"다음과 같이 인자를 전달 받는 함수를 만들 수 있다.
전역변수
function print_filename {
first_filename=$1
}
print_filename "LOTR.txt" "model.txt"
echo $first_filename
[output]
LOTR.txt전역변수를 제한하라면 local 명령을 사용합니다.
function print_filename {
local first_filename=$1
}
print_filename "LOTR.txt" "model.txt"
echo $first_filename
[output]
[blank]Returning value
function convert_temp {
echo $(echo "scale=2; ($1 - 32) * 5 / 9" | bc)
}
converted=$(convert_temp 30)
echo "30F in Celsius is $converted C"Scheduling your scripts
cron 이란? 시간을 뜻하는 그리스어 chronos에서 유래되었습니다.
crontab -l: 를이용해서 현재 작업(cronjob)이 뭐가 있는지 알 수 있습니다.
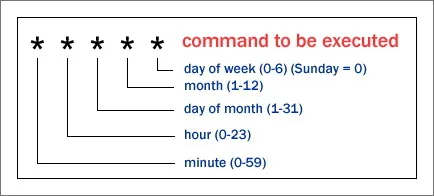
# Create a schedule for 30 minutes past 2am every day
30 2 * * * bash script1.sh
# Create a schedule for every 15, 30 and 45 minutes past the hour
15,30,45 * * * * bash script2.sh
# Create a schedule for 11.30pm on Sunday evening, every week
30 23 * * 0 bash script3.sh