When a pod consumes all the space on a PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC), it’ll fail to attach. The fix? Increase the PVC size—no need to delete and recreate it.
Kubernetes has supported volume expansion since v1.11 (GA in 1.16). Given that most managed clusters run much newer versions, you’re likely covered.
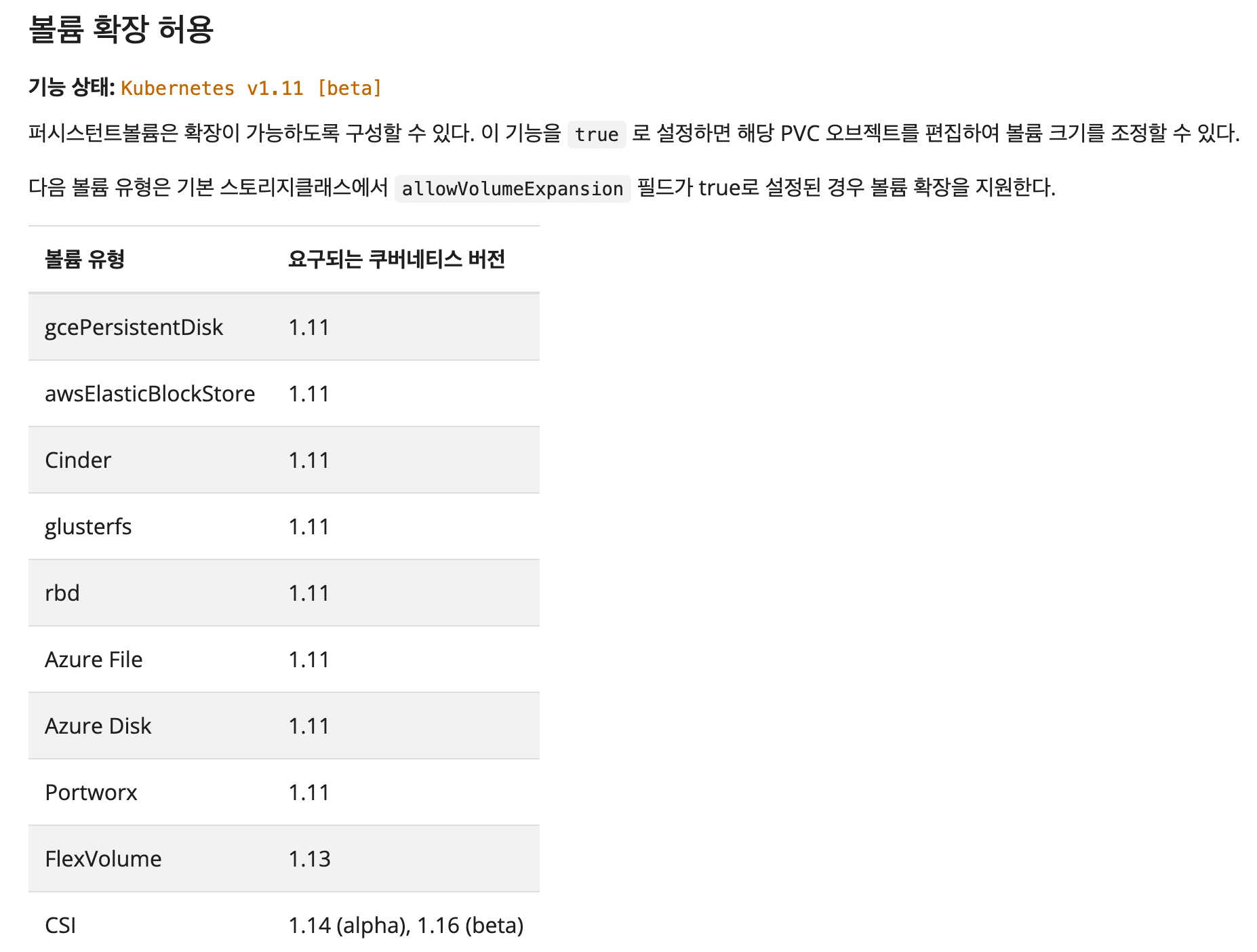
Step 1. Ensure the StorageClass Allows Expansion
PVCs must use a StorageClass with allowVolumeExpansion = true.
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: standard
provisioner: kubernetes.io/aws-ebs
parameters:
type: gp2
reclaimPolicy: Retain
allowVolumeExpansion: true
mountOptions:
- debug
volumeBindingMode: Immediate
If your StorageClass already exists, edit it to add allowVolumeExpansion: true.
Step 2. Edit the PVC
Increase the requested storage:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 200Gi # desired size
storageClassName: standard
status:
capacity:
storage: 200Gi
Save the change (e.g., kubectl edit pvc pvc). Kubernetes expands the underlying volume, and the pod can continue using it.
Note: you can scale up, but not down—plan your storage growth accordingly, especially in cloud environments where costs scale with capacity.