dbt (data build tool) focuses on the T in ELT, helping you transform data inside your warehouse with version-controlled SQL.
Recommended reading:
This walkthrough uses dbt to create marts in Google BigQuery.
1. Sample Data
Clone dbt Labs’ tutorial project:
git clone https://github.com/dbt-labs/jaffle_shop2. Install dbt
Follow the installation guide. On macOS:
brew tap dbt-labs/dbt
brew install dbt-bigquery
dbt --versionAdapters available: Postgres, Redshift, BigQuery, Snowflake, Apache Spark.
3. Create a GCP Service Account
dbt needs credentials to access BigQuery. You can authenticate via OAuth or a service account; I used the latter.
In the Google Cloud console:
- Create a service account.
- Grant:
BigQuery Data EditorBigQuery User
- Generate a JSON key and drop it into the
jaffle_shopdirectory.
Also create a BigQuery dataset (e.g., dbt).
4. Initialize dbt
Inside the repo:
dbt initChoose adapter bigquery, auth method service_account, and provide keyfile path, project ID, dataset, etc.
Settings are saved to ~/.dbt/profiles.yml. Validate:
dbt debugIf you prefer to predefine values, create profile_template.yml:
fixed:
dataset: dbt
job_execution_timeout_seconds: 300
keyfile: sharp-voyage-345407-16836b6fad46.json
location: US
method: service-account
project: sharp-voyage-345407
type: bigquery
threads: 15. Seed Data
seeds/ contains three CSVs (raw_customers, raw_orders, raw_payments). Load them into BigQuery:
dbt seedCheck BigQuery—the tables should appear.
6. Models
Project structure:
models/
├── customers.sql
├── orders.sql
├── docs.md
├── overview.md
├── schema.yml
└── staging/
├── stg_customers.sql
├── stg_orders.sql
├── stg_payments.sql
└── schema.ymlThe schema.yml describes models and their columns/tests:
version: 2
models:
- name: customers
description: Basic customer info plus derived metrics.
columns:
- name: customer_id
tests:
- unique
- not_null
# …SQL models transform staging tables into marts using familiar SQL:
{% raw %}
with customers as (select * from {{ ref('stg_customers') }}),
orders as (select * from {{ ref('stg_orders') }}),
payments as (select * from {{ ref('stg_payments') }}),
customer_orders as (
select customer_id,
min(order_date) as first_order,
max(order_date) as most_recent_order,
count(order_id) as number_of_orders
from orders
group by customer_id
),
customer_payments as (
select orders.customer_id,
sum(amount) as total_amount
from payments
left join orders on payments.order_id = orders.order_id
group by orders.customer_id
),
final as (
select
customers.customer_id,
customers.first_name,
customers.last_name,
customer_orders.first_order,
customer_orders.most_recent_order,
customer_orders.number_of_orders,
customer_payments.total_amount as customer_lifetime_value
from customers
left join customer_orders on customers.customer_id = customer_orders.customer_id
left join customer_payments on customers.customer_id = customer_payments.customer_id
)
select * from final{% endraw %}
Run the models:
dbt run7. Tests
dbt can validate data quality. schema.yml tests (e.g., unique, not_null) execute via:
dbt testSample output:
Finished running 20 tests … PASS=20 WARN=0 ERROR=0 SKIP=0 TOTAL=20If a test fails (e.g., unique on first_name), dbt shows the failing test and the compiled SQL query.
8. Documentation UI
Generate browsable documentation:
dbt docs generate
dbt docs serveOpen the local web UI to explore lineage, models, columns, and tests.
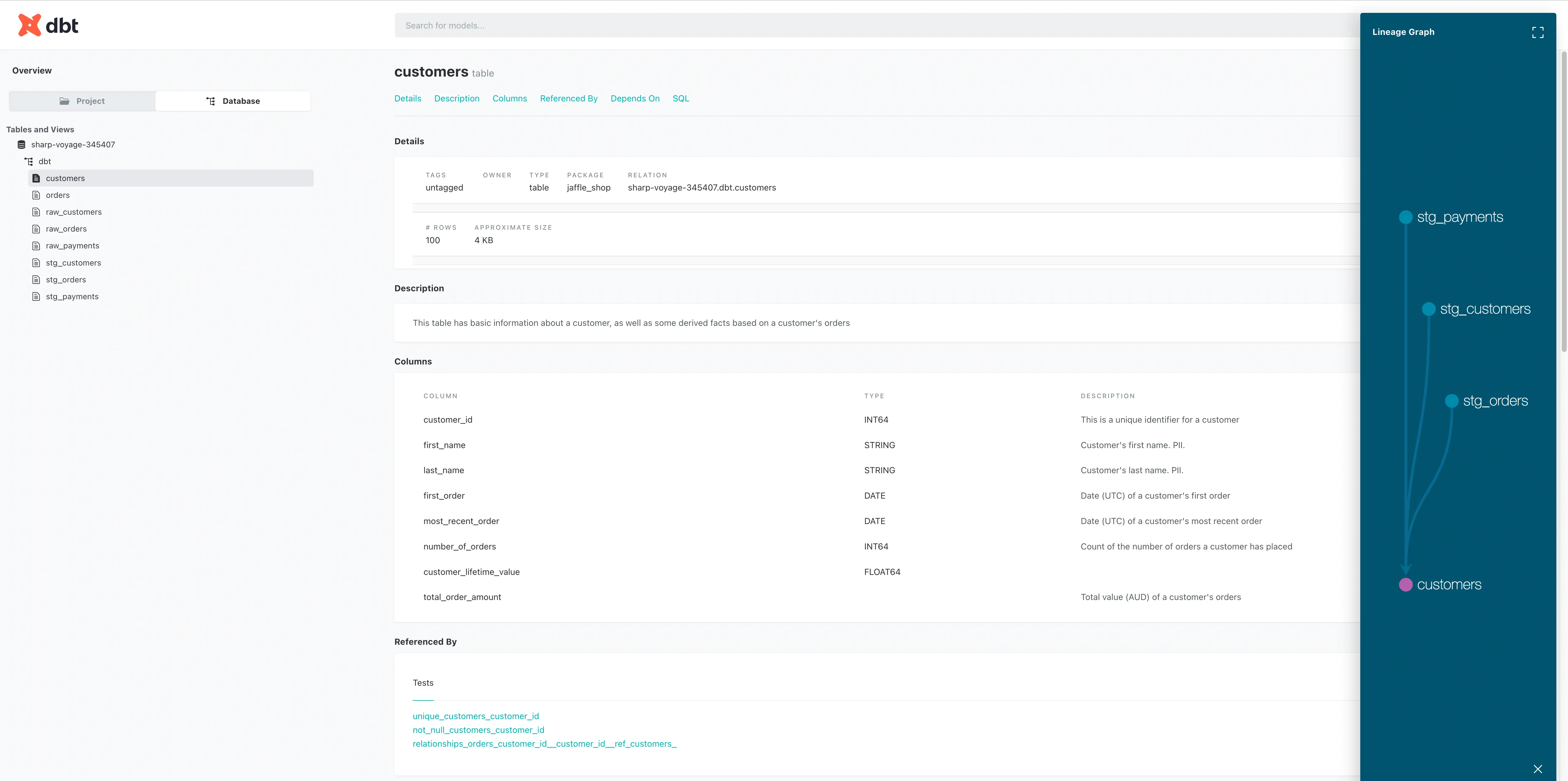
dbt makes it straightforward to build, test, and document transformations directly in the warehouse. There’s plenty more to learn, but even this basic workflow highlights its power.
