Unit Testing Basics
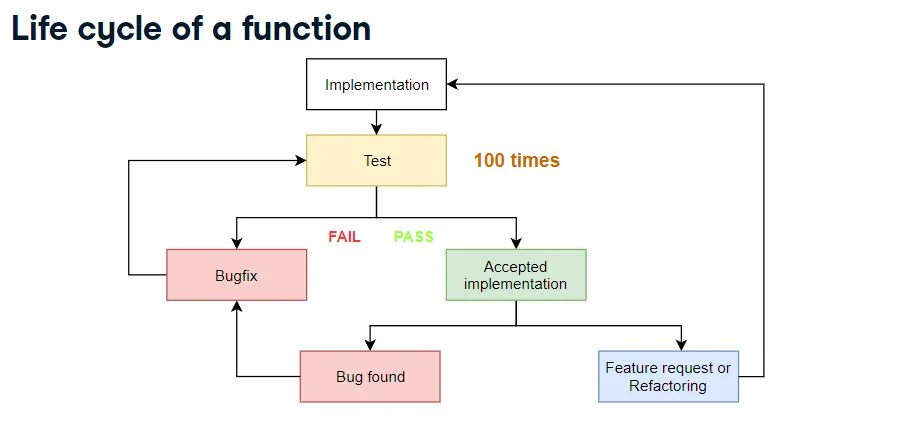
Interactive experiments in a REPL work, but they’re inefficient when you have to repeat them dozens or hundreds of times.
Source: DataCamp – Unit Testing for Data Science in Python
Imagine cleaning rows in a TSV dataset:
area (sq. ft.) price (dollars)
2,081 314,942
1,059 186,606
293,410
1,148 206,186
1,463238,765If a row is missing the area or the tab delimiter, it’s invalid.
def row_to_list(row):
...| Argument | Type | Return value |
|---|---|---|
"2,081\t314,942\n" | Valid | ["2,081", "314,942"] |
"\t293,410\n" | Invalid | None |
"1,463238,765\n" | Invalid | None |
Manually calling the function for every possible row is tedious. Automated unit tests save time—and they’re essential skills for data scientists.
Python Unit Testing Libraries
pytestunittestnosedoctest
Why pytest?
- Simple to use.
- Popular and well supported.
- Covers all the core testing features you need.
Step 1. Create a Test File
Name the file test_row_to_list.py. When a file name starts with test_, pytest treats it as a test module rather than normal application code.
Step 2. Imports
In test_row_to_list.py, import pytest and the function under test (row_to_list).
Step 3. Unit Tests Are Python Functions
import pytest
import row_to_list
def test_for_clean_row():
...Tests are regular Python functions whose names start with test_.
Step 4. Assertions
assert boolean_expressionIf the expression is True, pytest prints nothing and the assertion passes. If it’s False, Python raises AssertionError and the test fails.
import pytest
import row_to_list
def test_for_clean_row():
assert row_to_list("2,081\t314,942\n") == ["2,081", "314,942"]If there’s a bug, the assertion fails and pytest shows the error.
Add more cases:
def test_for_missing_area():
assert row_to_list("\t293,410\n") is None
def test_for_missing_tab():
assert row_to_list("1,463238,765\n") is NoneRemember to compare with is None, not == None.
Step 5. Run the Tests
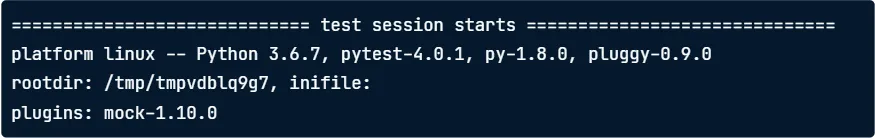
pytest test_row_to_list.pyReading Pytest Output
-
General info: OS, Python version, pytest version, working directory, plugins.
-
Collected tests: e.g.
collected 3 itemsfollowed bytest_row_to_list.py.
.means the test passed.Fmeans the test failed (usually due to an exception).
-
Failure details: pytest shows the failing line marked with
>, followed by the exception (prefixed withE) and the evaluated values.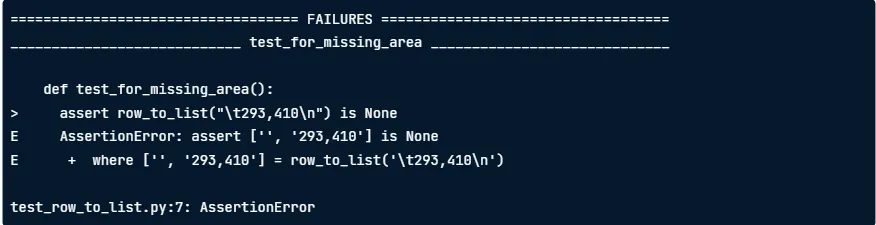
-
Summary: total fail / pass count.

Benefits of Unit Tests
- Save time by automating repetitive checks.
- Document expected behavior—tests double as executable examples.
- Increase confidence for users of your package.
- Reduce production downtime when tied into CI pipelines (failed tests block deployments).
What Counts as a “Unit”?
- A small, independent piece of code.
- Typically a single Python function or class.
Mastering Assertions
assert boolean_expression, message
assert 1 == 2, "One is not equal to two!"
# Raises AssertionError: One is not equal to two!Including a message makes failures easier to understand.
def test_for_missing_area_with_message():
actual = row_to_list("\t293,410\n")
expected = None
message = (
"row_to_list('\\t293,410\\n') returned {0} instead of {1}"
.format(actual, expected)
)
assert actual is expected, message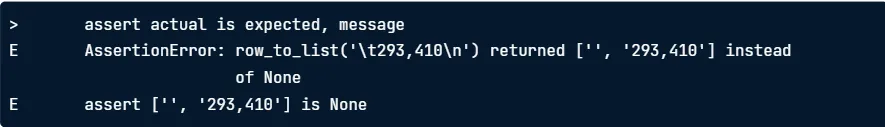
Beware floating-point comparisons:
0.1 + 0.1 + 0.1 == 0.3 # False
0.1 + 0.1 + 0.1 # 0.30000000000000004Use pytest.approx for tolerant comparisons:
assert 0.1 + 0.1 + 0.1 == pytest.approx(0.3)
assert np.array([0.1 + 0.1, 0.1 + 0.1 + 0.1]) == pytest.approx(np.array([0.2, 0.3]))Type checks:
def test_on_string_with_one_comma():
return_value = convert_to_int("2,081")
assert isinstance(return_value, int)
assert return_value == 2081Testing Exceptions Instead of Return Values
split_into_training_and_testing_sets should accept a 2D NumPy array, split 75% / 25%, and return the two arrays.
example_argument = np.array([
[2081, 314942],
[1059, 186606],
[1148, 206186],
])
split_into_training_and_testing_sets(example_argument)But if you pass a 1D array, it should raise ValueError.
def test_valueerror_on_one_dimensional_argument():
example_argument = np.array([2081, 314942, 1059, 186606, 1148, 206186])
with pytest.raises(ValueError):
split_into_training_and_testing_sets(example_argument)Capture the exception for further inspection:
with pytest.raises(ValueError) as exception_info:
split_into_training_and_testing_sets(example_argument)
assert exception_info.match(
"Argument data array must be two dimentional."
"Got 1 dimensional array instead!"
)The Well-Tested Function
More test cases inspire more confidence:
| Rows (input) | Training rows (int(0.75 * n)) | Testing rows (n - ...) |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | 6 | 2 |
| 10 | 7 | 3 |
You can’t cover every possible input, but aim for representative categories.
Categorizing Arguments
- Bad arguments: e.g. one-dimensional arrays → expect exceptions.
- Special arguments: boundary cases; inputs triggering special logic.
- Normal arguments: typical, valid inputs.
Testing each category dramatically improves coverage.
Test-Driven Development (TDD)
Feature work often comes first and testing gets postponed indefinitely. Flip the order:
- Write unit tests and nail down requirements.
- Run them (they should fail—no implementation yet).
- Implement the function and rerun the tests until they pass.
Organizing a Growing Test Suite
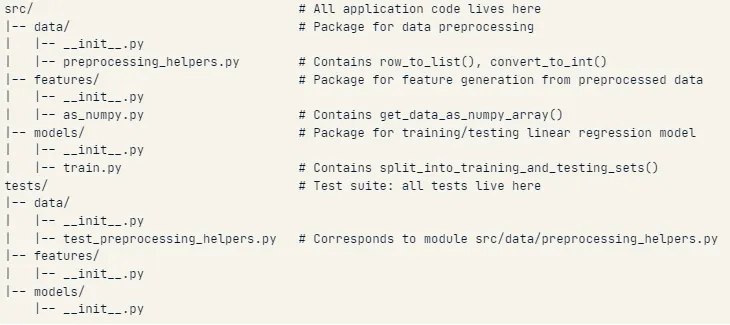
Split related tests into their own modules and group them by class.
import pytest
from data.preprocessing_helpers import row_to_list, convert_to_int
class TestRowToList(object):
def test_on_no_tab_no_missing_value(self):
...
def test_on_two_tabs_no_missing_value(self):
...
class TestConvertToInt(object):
def test_with_no_comma(self):
...
def test_with_one_comma(self):
...Mastering Test Execution
Pytest can discover and run every test in a directory tree.
cd tests
pytestPytest recursively searches the working directory:
- Files starting with
test_→ test modules. - Classes starting with
Test→ test classes. - Functions starting with
test_inside those classes → unit tests.
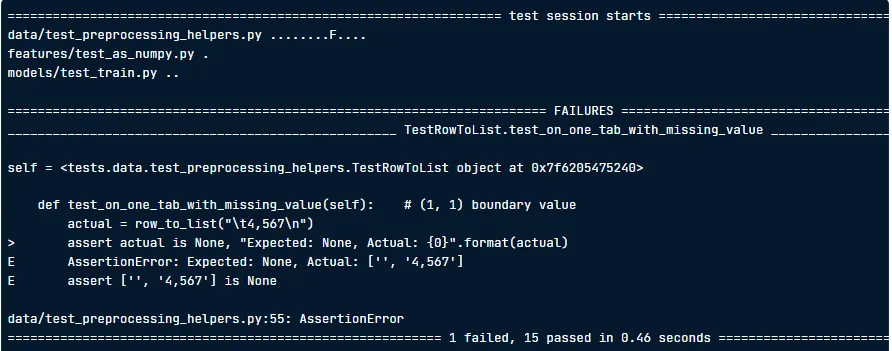
Other useful commands:
pytest -x→ stop after the first failure.pytest data/test_preprocessing_helpers.py→ run a specific file.
Node IDs
- Test class:
<path_to_module>::<TestClass> - Individual test:
<path_to_module>::<TestClass>::<test_function>
Run by node ID:
pytest data/test_preprocessing_helpers.py::TestRowToList